GitHub is the largest code host in the world, with 20+ million users. It’s also the place where the open source community offers access to most of its projects. We have had plenty of requests for GitHub integration and today we are excited to announce support for exporting RootCause errors to GitHub. This feature (available for Business customers) allows you to export any logged error to GitHub, and it is available in two modes: manual and automatic.
Manual export mode
In manual mode, you choose which errors to export and do it manually by specifying the GitHub repository name and then click the Export button as seen below.

This opens the Export dialog where you can enter the GitHub user and repo where you want the issue to be created.

After doing this, a new GitHub issue is created, the screenshot is embedded into the issue and a special ‘Runtime error’ label is added.

The Automatic mode
There is also a second, automatic mode. It will create a new (or update an existing) GitHub issue every time an error is logged by RootCause. Please note that this mode creates just one GitHub issue per error. When the same error happens multiple times, the issue is updated so you always know how many times it occurred. If you think that an error is not significant for your project, just close the issue. Any future similar errors will update the issue stats, but it will not distract you from real problems. The automatic mode allows developers to keep using GitHub issues as the primary place of all your bug reports, and use RootCause to store the additional debugging context (video replay, live replay etc).
In order to activate the automatic mode, simply follow these steps:
First, let’s open an application and edit its settings:
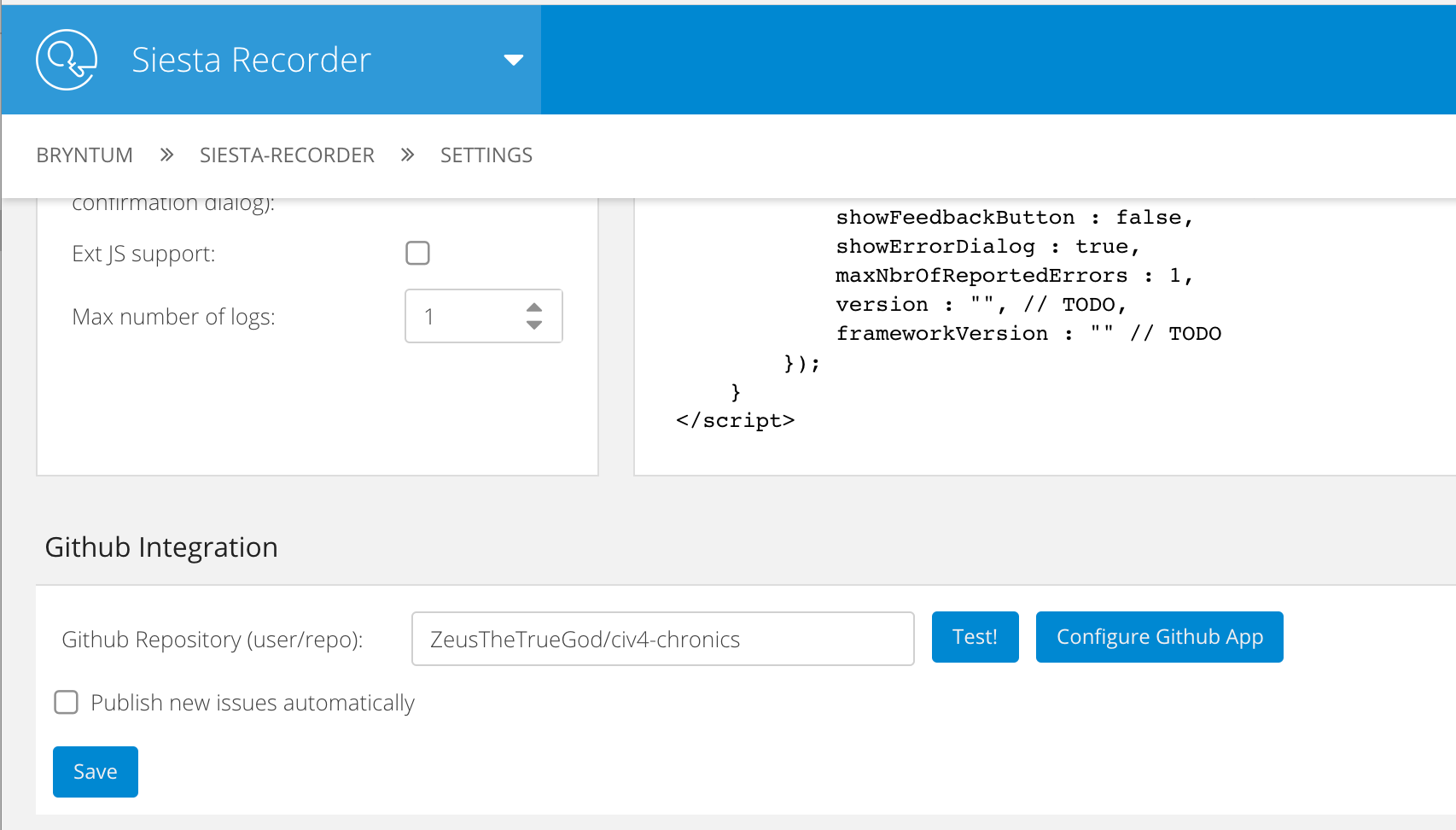
Next, we need to update the repository name and check the ‘Publish new issues automatically’ checkbox.
Please note that before updating settings, you need to ensure that you have authorized the RootCause GitHub app for your repository. All you need to do is to click on ‘Configure GitHub App’, install the app into your GitHub account and specify which repositories should become accessible to the RootCause app. After that, enter the repository name in the ‘user/repo’ format and press the Test button. In a few seconds you will get a response if the repo is accessible for our GitHub app or not.
We hope you’ll find the new GitHub integration useful, and please let us know what other features are important to you.


Leave a Reply